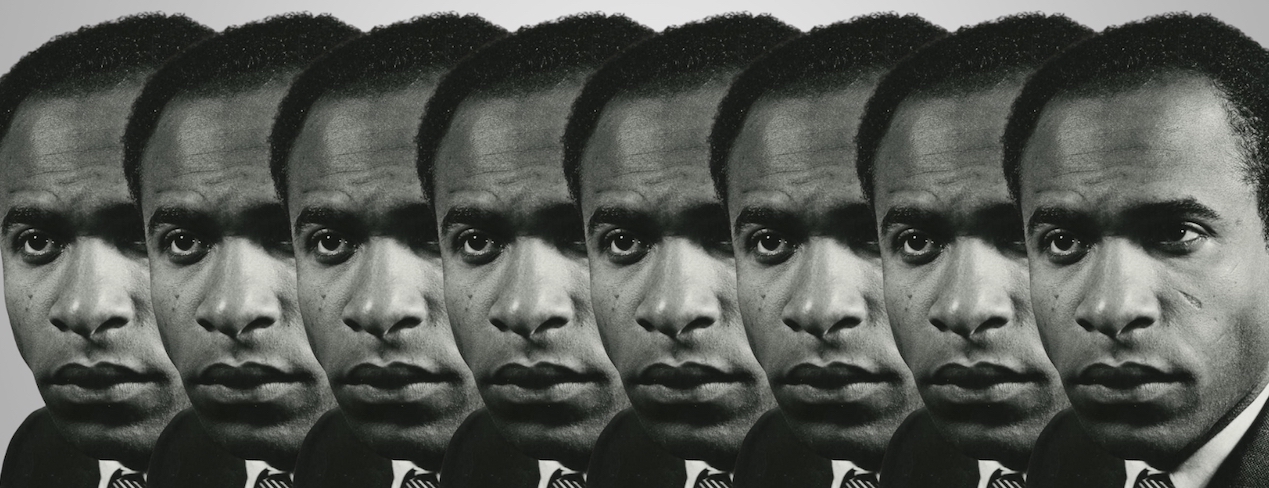
The Revolutionary Stranger: How Frantz Fanon Put Theory Into Practice
Adam Shatz on the Life and Legacy of a Great Post-Colonialism Thinker
In November 1960, a traveler of ambiguous origin, brown-skinned but not African, arrived in Mali. Issued in Tunis two years earlier, his passport identified him as a doctor born in 1925 in Tunisia, height: 165 cm, color of hair: black, color of eyes: black.
The pages were covered with stamps from Nigeria, Ghana, Liberia, Guinea, Italy. The name on the passport, a gift from the government of Libya, was Ibrahim Omar Fanon, a nom de guerre. The psychiatrist Frantz Fanon was not from Tunisia but from Martinique. He had not come to Mali to do medical work: he was part of a commando unit.
It had been a long journey by car from the Liberian capital of Monrovia: more than twelve hundred miles through tropical forest, savanna, and desert, and the eight-man team still had far to go. From the journal he kept, it’s clear that Fanon was mesmerized by the landscape. “This part of the Sahara is not monotonous,” he writes. “Even the sky up there is constantly changing. Some days ago, we saw a sunset that turned the robe of the sky a bright violet. Today it is a very hard red the eye encounters.” His entries move freely between rousing expressions of hope and somber reminders of the obstacles facing African liberation struggles. “A continent is on the move and Europe is languorously asleep,” he writes. “Fifteen years ago it was Asia that was stirring. Today 650 million Chinese, calm possessors of an immense secret, are building a world entirely on their own. The giving birth to a world.” And now an “Africa to come” could well emerge from the convulsions of anti-colonial revolution.
Yet “the specter of the West,” he warns, is “everywhere present and active.” His friend Félix-Roland Moumié, a revolutionary from Cameroon, had just been poisoned by the French secret service, and Fanon himself had narrowly escaped an attempt on his life on a visit to Rome. Meanwhile, a new superpower, the United States, had “plunged in everywhere, dollars in the vanguard, with [Louis] Armstrong as herald and Black American diplomats, scholarships, the emissaries of the Voice of America.”
Even as he turned violently against the colonial motherland, Fanon remained faithful to the ideals of the French Revolution.
Yet in the long run, Fanon believed, the African continent would have to reckon with threats more crippling than colonialism. On the one hand, Africa’s independence had come too late: rebuilding and giving a sense of direction to societies traumatized by colonial rule—societies that had long been forced to take orders from others and to see themselves through the eyes of their masters—would not be easy.
On the other hand, independence had come too early, empowering the continent’s narcissistic “national middle classes” who “suddenly develop great appetites.” He writes: “The deeper I enter into the cultures and political circles the surer I am that the great danger for Africa is the absence of ideology.”
Fanon recorded these impressions in a blue Ghana School Teachers Book No. 3 that he had picked up in Accra. It is now stored at the Institut Mémoires de l’édition contemporaine, a research library housed in a former monastery in Normandy that sheltered partisan fighters during the Second World War. To take it in one’s hands sixty years later and leaf through the pages is to inspect the thoughts of a dying man: Fanon did not yet know he had leukemia, or that his life would end in 1961 in a hospital in Maryland, in the heart of the American empire he despised. On the road in West Africa, he was open, thoughtful, and intrigued by the continent from which his ancestors had been carried on slave ships to the French colony of Martinique.
In Mali he imagined himself home, among his Black brothers, yet he remained a stranger. He had come as an undercover agent of a neighboring country in what he called “White Africa”: Algeria, then in the seventh year of its liberation struggle against French rule. The aim of his reconnaissance mission was to make contact with the desert tribes and open a southern front on Algeria’s border with Mali so that arms and ammunitions could be moved from the Malian capital of Bamako through the Sahara to the rebels of the Front de libération nationale (FLN).
The head of Fanon’s commando unit was a major in the FLN’s military wing, the Armée de libération nationale (ALN). He was a “funny chap” who went by the name of Chawki: “small, lean, with the implacable eyes of an old maquis fighter.” Fanon was impressed by the “intelligence and clarity of his ideas” and his knowledge of the Sahara, a “world in which Chawki moves with the boldness and the perspicacity of a great strategist.” Chawki, he tells us, spent two years studying in France but returned to Algeria to work his father’s land. When the war of liberation launched by the FLN began on November 1, 1954, he “took down his hunting rifle from its hook and joined the brothers.”
Not long after, Fanon, too, had joined “the brothers.” From 1955 until his expulsion from Algeria two years later, he had given sanctuary to rebels at the psychiatric hospital he directed in Blida-Joinville, just outside Algiers. He had provided them with medical care and taken every possible risk short of joining the maquisards in the mountains—his first impulse when the revolution broke out. No one believed more fervently in the rebels than the man from Martinique. He had gone on to join the FLN in exile in Tunis, identifying himself as an Algerian and preaching the cause of Algerian independence throughout Africa. Every word that he wrote paid tribute to the Algerian struggle.
But he could never really become an Algerian; he did not even speak Arabic or Berber (Amazigh), the languages of Algeria’s indigenous peoples. In his work as a psychiatrist, he often had to depend on interpreters. Algeria remained permanently out of reach for him, an elusive object of love, as it was for so many other foreigners who had been seduced by it—not least the European settlers who began arriving in the 1830s. He would be, at most, an adopted brother, dreaming of a fraternity that would transcend tribe, race, and nation: the kind of arrangement that France promised him as a young man and that had led him to join the war against the Axis powers.
France betrayed its promise, but even as he turned violently against the colonial motherland, Fanon remained faithful to the ideals of the French Revolution, hoping that they might be achieved elsewhere, in the independent nations of what was then known as the Third World. He was a “Black Jacobin,” as the Trinidadian Marxist C.L.R. James described Toussaint Louverture in his classic history of the Haitian Revolution.
Nearly six decades after the loss of Algeria, France still hasn’t forgiven Fanon’s “treason”: a recent proposal to name a street after him in Bordeaux was struck down. Never mind that Fanon had bled for France as a young man, then fought for Algeria’s independence in defense of classical republican principles, or that his writing continues to speak to the predicament of many young French citizens of Black and Arab descent who have been made to feel like strangers in their own country.
In 1908, Georg Simmel, a German Jewish sociologist, published an essay called “The Stranger.” The stranger, he writes, “is not a wanderer, who may come today and leave tomorrow. He comes today—and stays.” This was Fanon’s experience throughout his life: as a soldier in the French army, as a West Indian medical student in Lyon, as a Black Frenchman, and as a non-Muslim in the Algerian resistance to France. Simmel suggests that even as the stranger arouses suspicion, he benefits from a peculiar epistemological privilege since “he is offered revelations, confessions otherwise carefully hidden from any more organically embedded persons.”
Listening to such confessions was Fanon’s trade as a psychiatrist, and it was in doing so that he decided to throw himself into the independence struggle, even to become Algerian, as if a commitment to his patients’ care and recovery required an even more radical kind of solidarity, a marriage to the people he had come to love.
The twentieth century was, of course, full of foreign-born revolutionaries, radical strangers drawn to distant lands upon which they projected their hopes and fantasies. Yet Fanon was unusual, and much more than a sympathetic fellow traveler. He would eventually become the FLN’s roving ambassador in Africa—his complexion a decided asset for a North African movement seeking support from its sub-Saharan cousins—and acquire a reputation as the FLN’s “chief theoretician.”
This he was not. It would have been highly surprising if such an intensely nationalistic movement had chosen a foreigner as its theoretician. Fanon’s task was mostly limited to communicating aims and decisions that others had formulated. But he interpreted Algeria’s liberation struggle in a manner that helped transform it into a global symbol of resistance to domination. And he did so in the language of the profession he practiced, and at the same time radically reimagined: psychiatry.
Before he was a revolutionary, Fanon was a psychiatrist, and his thinking about society took shape within spaces of confinement: hospitals, asylums, clinics, and the prison house of race, which—as a Black man—he experienced throughout his life.
Fanon was not a modest man. He struck some of his contemporaries as vain, arrogant, even hotheaded. Yet to his patients he could hardly have been humbler.
What he saw in their faces, and in their physical and psychological distress, were people who had been deprived of freedom and forcibly alienated from themselves, from their ability to come to grips with reality and act upon it independently. Some of them were mentally ill (in French, aliénés); others were immigrant workers or colonized Algerians who suffered from hunger, poor housing, racism, and violence; still others suffered from performing the dirty work of colonial repression. (Fanon treated French soldiers who had tortured Algerian suspects, and wrote with remarkable lucidity and compassion about their traumas.) What they shared was an invisible, lacerating anguish inscribed in the psyche, immobilizing both body and soul. This anguish, for Fanon, was a kind of dissident knowledge: a counternarrative to the triumphal story that the West told about itself.
In a 1945 essay on Richard Wright’s memoir Black Boy, Ralph Ellison observed that racial oppression begins “in the shadow of infancy where environment and consciousness are so darkly intertwined as to require the skills of a psychoanalyst to define their point of juncture.” Fanon was a psychiatrist, not a psychoanalyst, but he read deeply in the literature of psychoanalysis.
His first book, Peau noire, masques blancs (Black Skin, White Masks), published in 1952, when he was twenty-seven, was an attempt to reveal the shadow that racial oppression cast across the lives of Black people. In his later writings on Algeria and the Third World, he powerfully evoked the dream life of societies disfigured by racism and colonial subjugation.
“History,” in the words of the Marxist literary critic Fredric Jameson, “is what hurts, it is what refuses desire and sets inexorable limits to individual as well as collective praxis.” Fanon had a rare gift for expressing the hurts that history had caused in the lives of Black and colonized peoples, because he felt those hurts with almost unbearable intensity himself. Few writers have captured so vividly the lived experience of racism and colonial domination, the fury it creates in the minds of the oppressed—or the sense of alienation and powerlessness that it engenders.
To be a Black person in a white majority society, he writes in one of his bleakest passages, was to feel trapped in “a zone of nonbeing, an extraordinarily sterile and arid region, an incline stripped bare of every essential from which a new departure can emerge.”
Like any struggle to exorcise history’s ghosts and wipe the slate clean, Fanon’s was often a confrontation with impossibility.
Yet Fanon himself had a fervent belief in new departures. In his writing, as well as in his work as a doctor and a revolutionary, he remained defiantly hopeful that the colonized victims of the West—the “wretched of the earth,” he called them—could inaugurate a new era in which they would be free not only of foreign rule but also of forced assimilation to the values and languages of their oppressors. But first they had to be willing to fight for their freedom. He meant this literally. Fanon believed in the regenerative potential of violence.
Armed struggle was not simply a response to the violence of colonialism; it was, in his view, a kind of medicine, rekindling a sense of power and self-mastery. By striking back against their oppressors, the colonized overcame the passivity and self-hatred induced by colonial confinement, cast off the masks of obedience they had been forced to wear, and were reborn, psychologically, as free men and women.
But, as he knew, masks are easier to put on than to cast off. Like any struggle to exorcise history’s ghosts and wipe the slate clean, Fanon’s was often a confrontation with impossibility, with the limits to his visionary desires. Much of the power of his writing resides in the tension, which he never quite resolved, between his work as a doctor and his obligations as a militant, between his commitment to healing and his belief in violence.
Fanon made his case for violence in his final work, Les Damnés de la terre (The Wretched of the Earth), published just before his death in December 1961. The aura that still surrounds him today owes much to this book, the culmination of his thinking about anti-colonial revolution and one of the great manifestos of the modern age. In his preface, Jean-Paul Sartre wrote that “the Third World discovers itself and speaks to itself through this voice.” An exaggeration, to be sure, and an inadvertently patronizing one: Fanon’s voice was one among many in the colonized world, which had no shortage of writers and spokespeople.
Yet the electrifying impact of Fanon’s book on the imagination of writers, intellectuals, and insurgents in the Third World can hardly be overestimated. A few years after Fanon’s death, Orlando Patterson—a radical young Jamaican writer who would later become a distinguished sociologist of slavery—described The Wretched of the Earth as “the heart and soul of a movement, written, as it could only have been written, by one who fully participated in it.”
The Wretched of the Earth was required reading for revolutionaries in the national liberation movements of the 1960s and ’70s. It was translated widely and cited worshipfully by the Black Panthers, the Black Consciousness movement in South Africa, Latin American guerrillas, the Palestine Liberation Organization, and the Islamic revolutionaries of Iran. From the perspective of his readers in national liberation movements, Fanon understood not only the strategic necessity of violence but also its psychological necessity. And he understood this because he was both a psychiatrist and a colonized Black man.
Some readers in the West have expressed horror at Fanon’s defense of violence, accusing him of being an apologist for terrorism—and there is much to contest. Yet Fanon’s writings on the subject are easily misunderstood or caricatured. As he repeatedly pointed out, colonial regimes, such as French-ruled Algeria, were themselves founded upon violence: the conquest of the indigenous populations; the theft of their land; the denigration of their cultures, languages, and religions.
The violence of the colonized was a counter-violence, embraced after other, more peaceful forms of opposition had proved impotent. However gruesome it sometimes was, it could never match the violence of colonial armies, with their bombs, torture centers, and “relocation” camps.
Readers with an intimate experience of oppression and cruelty have often responded sympathetically to Fanon’s insistence on the psychological value of violence for the colonized. In a 1969 essay, the philosopher Jean Améry, a veteran of the Belgian anti-fascist resistance and a Holocaust survivor, wrote that Fanon described a world that he knew very well from his time in Auschwitz. What Fanon understood, Améry argued, was that the violence of the oppressed is “an affirmation of dignity,” opening onto a “historical and human future.”
That Fanon, who never belonged anywhere in his lifetime, has been claimed by so many as a revolutionary brother—indeed, as a universal prophet of liberation—is an achievement he might have savored.
__________________________________

Excerpted from The Rebel’s Clinic: The Revolutionary Lives of Frantz Fanon by Adam Shatz. Published by Farrar, Straus and Giroux, an imprint of Macmillan. Copyright © 2024 by Adam Shatz. All rights reserved.
Adam Shatz
Adam Shatz is the US editor of the London Review of Books and a contributor to The New York Times Magazine, The New York Review of Books, The New Yorker, and other publications. He is the author of Writers and Missionaries: Essays on the Radical Imagination and the host of the podcast Myself with Others. He lives in Brooklyn, New York.